Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VFBs) are an emerging energy storage technology with significant potential, particularly in large-scale, long-duration storage applications. Unlike conventional rechargeable battery storage, VFBs use a vanadium electrolyte solution for both the positive and negative electrodes, making them unique in design and operation.
What Is Vanadium Redox Flow Battery?
The vanadium redox battery (VRB), also known as the vanadium flow battery (VFB) or vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), is a type of rechargeable flow battery.
It utilizes vanadium ions in various oxidation states to store and release electrical energy. Unlike conventional batteries, VRFBs store energy in liquid electrolytes that circulate through the system rather than in solid electrodes. This design allows for scalable and flexible energy storage solutions.
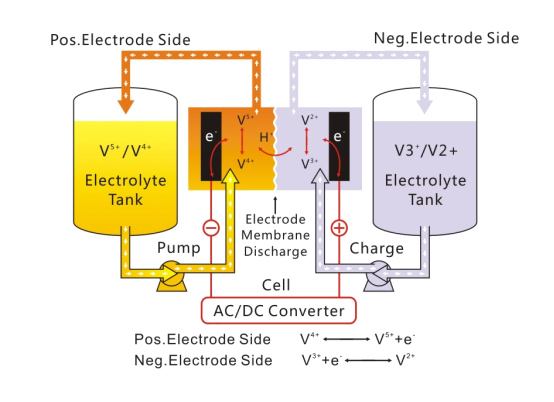
Key Components of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
| Key Component |
Description |
| Electrolytes |
- VRFB uses two liquid electrolytes, typically containing vanadium in different oxidation states (V²⁺, V³⁺, V⁴⁺, and V⁵⁺). |
| Electrodes |
- Two electrodes (usually carbon or similar materials) facilitate the redox reactions (reduction and oxidation) to release or store energy. |
| Membrane |
- A proton-conducting membrane (often made of Nafion) separates the two electrolyte solutions, allowing ion flow between the two sides during the charge/discharge cycle. |
| Pumps and Flow System |
- These components circulate the electrolytes through the electrochemical cell, ensuring continuous flow of vanadium ions for the energy conversion process. |
How Does a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Works?
- 1. Discharge Cycle
- During discharge, vanadium ions in the positive and negative electrolyte solutions undergo oxidation and reduction reactions at the electrodes, releasing electrical energy.
- 2. Charge Cycle
- During charging, energy is stored by reversing the oxidation and reduction reactions, moving vanadium ions back to their original oxidation states. This process involves applying an external current to the system.
- 3. Flowing Electrolytes
- The key characteristic of flow batteries is the use of liquid electrolytes that are pumped through the system, which allows the battery's capacity to be easily increased by simply enlarging the size of the electrolyte storage tanks.
Advantages Of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
- √ Scalability
VRFBs can be easily scaled up by increasing the size of the electrolyte tanks, making them ideal for large-scale energy storage applications such as grid balancing and renewable energy storage. - √ Long Cycle Life
Vanadium does not degrade during cycling (because it uses the same material for both positive and negative electrolytes), which gives VRFBs a longer operational life compared to other battery chemistries.
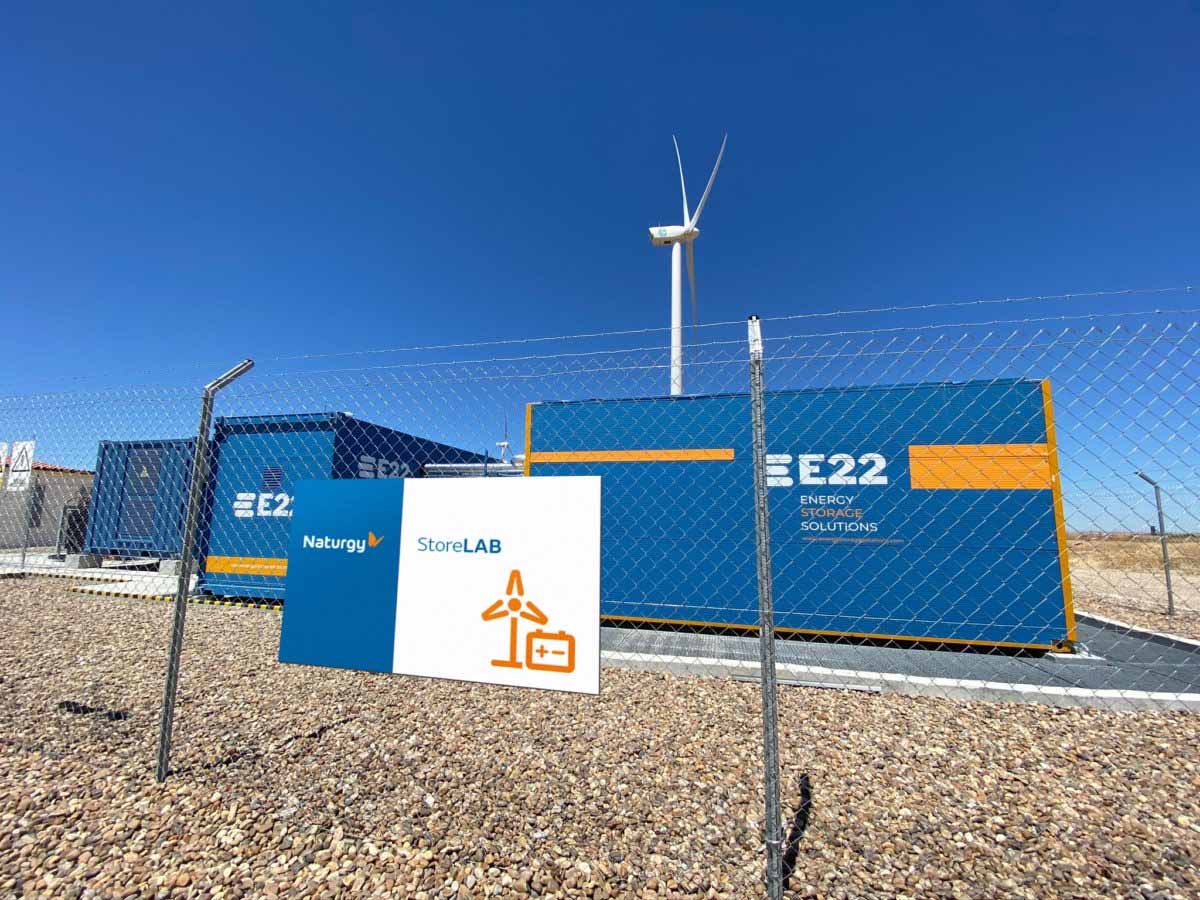

Naturgy deployed this vanadium flow battery in Zamora, Spain.
- √ Safety
VRFBs are relatively safe because the electrolytes are non-flammable and non-toxic. The liquid form also reduces the risk of thermal runaway, which can be a concern in some other types of batteries. - √ Efficiency
VRFBs can have round-trip efficiencies (the percentage of energy recovered during discharging) ranging from 65% to 85%, depending on the design and operating conditions. -
√ Energy and Power Decoupling
VRFBs can independently scale the energy (size of electrolyte tanks) and power (size of the electrochemical cell) components, which gives them flexibility for different applications.
Applications Of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
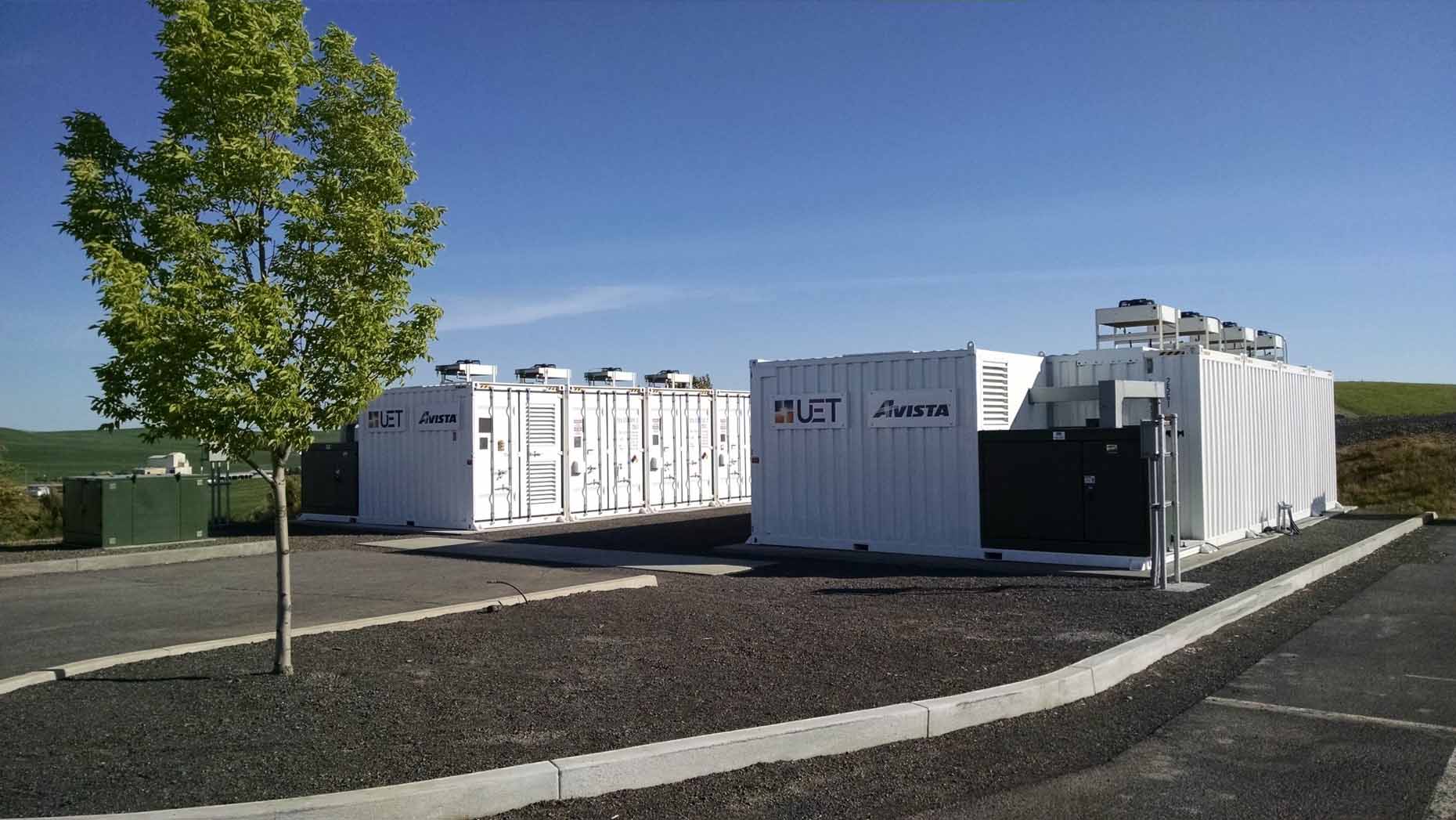

The 1 MW 4 MWh containerized vanadium flow battery owned by Avista Utilities and manufactured by UniEnergy Technologies.
- ⭐ Grid Storage: VRFBs are particularly useful for storing excess energy from renewable sources like wind and solar, providing a buffer to smooth out the intermittency of these energy sources.
- ⭐ Renewable Energy Integration: They can store energy when demand is low and release it during peak demand hours.
- ⭐ Backup Power: VRFBs can also be used for backup power systems in critical infrastructure.
Vanadium Redox Flow Battery VS Lithium Ion Battery
|
Feature |
Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VFB) |
|
|
Safety |
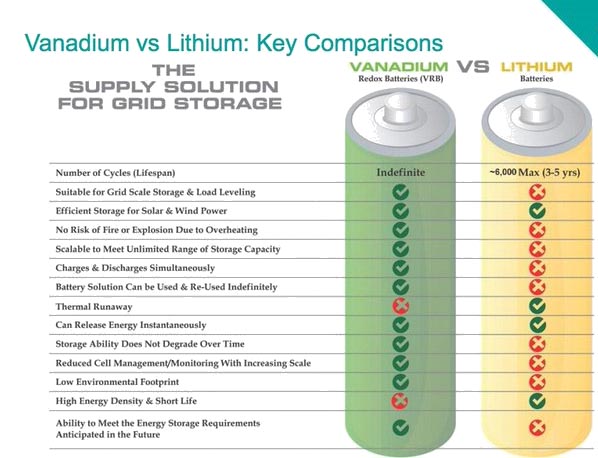
Inherently safer due to aqueous electrolyte solutions, no thermal runaway, fires, or explosions. |
Can pose safety risks, including thermal runaway, fires, or explosions if damaged or overheated. |
|
Scalability |
Easily scalable, allowing for modular expansion suitable for large storage facilities (hundreds of MWh). |
Less scalable; typically used in fixed-size units, although it can be scaled for some applications. |
|
Initial Cost |
Higher upfront investment compared to Li-ion batteries. |
Lower upfront cost compared to VFBs. |
|
Energy Density |
Lower energy density (12-40 Wh/kg), making them unsuitable for mobile applications like EVs. |
Higher energy density (80-300 Wh/kg), ideal for mobile applications like electric vehicles (EVs). |
|
Energy Conversion Efficiency |
Lower efficiency (70-75%) compared to Li-ion batteries. |
Higher efficiency (90%) due to more efficient charge/discharge cycles. |
|
Cycle Life |
Extremely long cycle life (>10,000 cycles, with some exceeding 20,000 cycles). |
Shorter cycle life (usually 1,000-3,000 cycles, depending on battery type and usage). |
|
Lifetime Costs |
Lower cost per Watt-Hour (Wh) over the entire lifecycle. More environmentally friendly with recyclable vanadium electrolytes. |
Higher lifetime cost per watt-hour due to shorter cycle life and degradation over time. |
|
Cost Per Wh |
Currently around $0.30-$0.40 per Wh, more cost-effective for long-term energy storage. |
Typically $0.50 per Wh, higher cost for long-term storage due to shorter cycle life and faster degradation. |
▲Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VFBs) are more suitable for large-scale, long-duration energy storage applications due to their safety, scalability, long cycle life, and cost efficiency over the long term. However, their low energy density and high initial cost make them unsuitable for applications like electric vehicles.
▲ Lithium-ion Batteries (Li-ion) are more widely used for portable applications like electric vehicles due to their higher energy density, but they come with safety risks, shorter cycle life, and higher long-term costs compared to VFBs.
Top 10 Vanadium Flow Battery Companies
There are several companies and organizations worldwide working on the development and commercialization of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs), with a focus on large-scale energy storage solutions. Some key players in the VRFB market include both established companies and startups specializing in this technology.
1. RedT Energy (now Invinity Energy Systems)
- Location: United Kingdom
- Overview: RedT Energy merged with HydroStar to form Invinity Energy Systems. They specialize in long-duration energy storage solutions based on VRFB technology. Their products are aimed at industrial and grid-scale energy storage applications.
2. VRB Energy
- Location: China / Canada
- Overview: VRB Energy is a subsidiary of China's State Grid Corporation and focuses on the development and commercialization of VRFBs. They offer large-scale energy storage solutions and are particularly active in both China and international markets.
3. Sumitomo Electric Industries
- Location: Japan
- Overview: Sumitomo has been a significant player in the development of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery technology. The company has developed its own VRFB systems and has implemented them in various energy storage projects, particularly in the Japanese market.
- Location: United States
- Overview: Imergy Power Systems specializes in developing vanadium-based flow batteries for grid-scale energy storage. The company is focused on integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind with energy storage.
5. Sivens
- Location: France
- Overview: Sivens is a French company involved in the production of VRFB systems for energy storage. They focus on developing cost-effective, long-lasting energy storage solutions for both commercial and industrial applications.
- Location: Canada
- Overview: VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. is a Canadian mining and technology company that focuses on the extraction of vanadium and the development of VRFB technology. The company is working on improving the efficiency of vanadium extraction and developing new applications for VRFBs.
7. Energy Storage Systems (ESS, Inc.)
- Location: United States
- Overview: ESS Inc. is a company focused on long-duration energy storage solutions using iron flow battery technology, which is similar to VRFB but uses iron instead of vanadium. They provide large-scale energy storage solutions, but their work is part of the growing market of flow batteries.
8. CellCube Energy Storage Systems
- Location: Austria / Canada
- Overview: CellCube, a subsidiary of Gildemeister Energy Storage, focuses on manufacturing and deploying Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries for grid-scale storage. The company is particularly involved in large-scale energy storage projects in Europe and North America.
9. Renewable Energy Solutions (RES Group)
- Location: United Kingdom
- Overview: RES Group, a large global renewable energy player, is working on integrating vanadium flow batteries into energy systems as part of their goal to develop sustainable, large-scale energy storage solutions for renewables.
10. Pu Neng (PNT)
- Location: China
- Overview: Pu Neng (PNT) is a Chinese company that develops and manufactures Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries for both small and large-scale energy storage solutions. They focus on integrating VRFBs into renewable energy systems.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries offer promising advantages, there are some challenges that need to be addressed:
- ● Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Price: The cost of vanadium and the infrastructure required for large-scale VFB systems can be relatively high. However, as the technology matures and vanadium production scales up, costs are expected to decrease.
- ● Energy Density: While VFBs have excellent long-duration capabilities, their energy density (the amount of energy stored per unit volume or weight) is lower than that of lithium-ion or solid-state batteries. This can make them less suitable for applications where space and weight are critical.
- ● Efficiency: The efficiency of VFBs, while high, is still slightly lower than that of lithium-ion batteries. However, improvements in materials and design are expected to enhance the efficiency over time.
Conclusion
The Vanadium Redox Flow Battery is an innovative and promising energy storage solution with the potential to revolutionize large-scale energy storage systems. Its scalability, long cycle life, safety, and environmentally friendly design make it an attractive option for grid storage, renewable energy integration, and other large-scale energy storage applications. As the technology matures and cost reductions are realized, VFBs could play a key role in the future of sustainable energy storage, helping to create a more resilient and reliable energy grid.
Post time: Jan-07-2025

